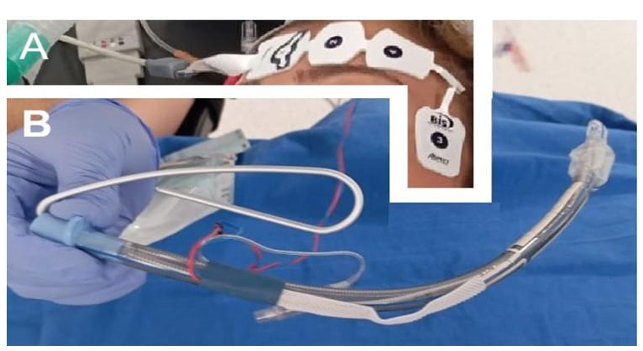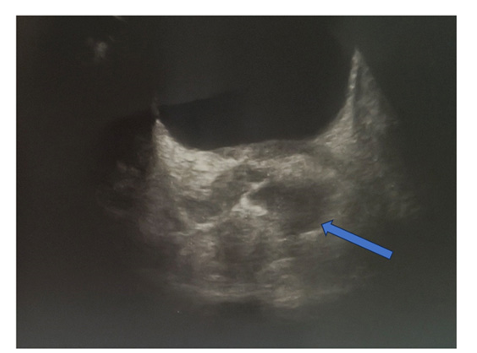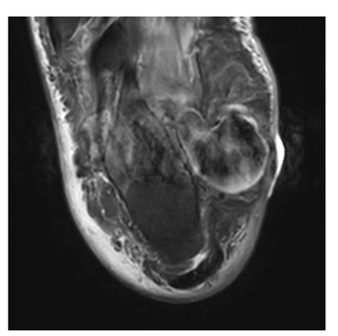
1. Abstract
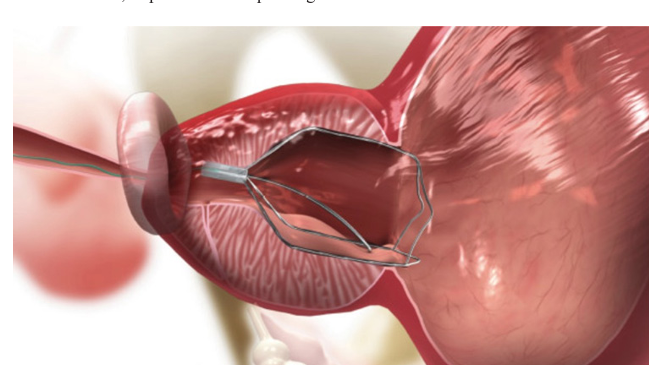
Aortic dissection is a life-threatening cardiovascular condition characterized by the separation of the aortic wall layers due to an intimal tear.
Reactive Attachment Disorder (RAD), only diagnosed in the context of early abuse and neglect, is characterised by failure to seek and accept comfort. It involves lack of activation of the – developmentally essential – attachment system, hence has profound developmental disadvantages. RAD usually resolves quickly in the context of adequate care and has been assumed never to persist once the child is in a nurturing placement.
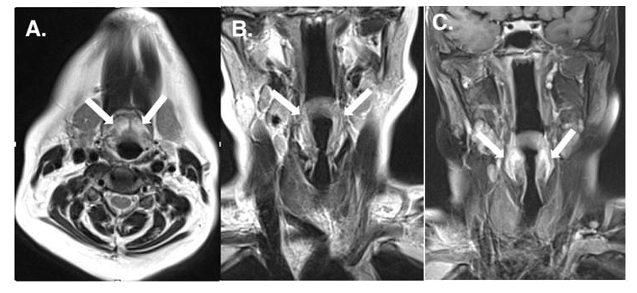
We report a rare case of a teenager presenting with progressive contralateral extremity paresis and numbness caused by posterolateral disc herniation at C3-C4. Intervertebral decompression and artificial disc replacement was performed. Follow-up at 2 months showed complete neurologic recovery.
In July 2017 we observed, in our Internal Medicine Department, the patient F.A. recently affected by recurrent Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary disease (COPD). Anamnesis’ data have underlined the presence of Permanent Atria Fibrillation (FAP) and severe carotid stenosis, treated with carotid endarterectomises (2012).
Salivary gland calculi account for the most common disease of the salivary glands. The majority of sialoliths occur in the submandibular gland or its duct and are a common cause of acute and chronic infections. Sialolith can be unilateral, bilateral, single or multiple. Depending on the gland affected and stone location, there are various methods available for the management of salivary stones or calculi.
It was with great enthusiasm that we have seen the results published by Francis et al. concerning the adjuvant hormone therapy. In the SOFT study, the 8 year disease-free survival rate was 78.9% in patients who did only tamoxifen, 83.2% with tamoxifen and ovarian suppression, and 85.9% with exemestane and ovarian suppression
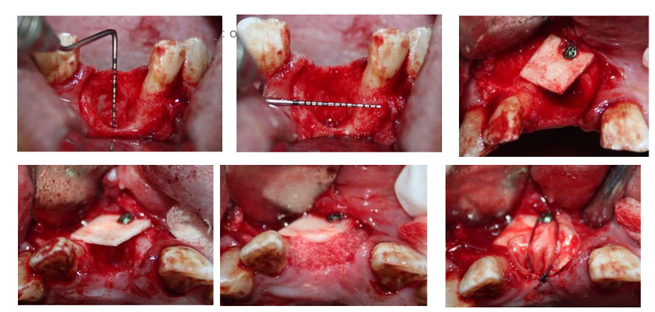
We describe a female patient in whom CT-guided hook wire marking enabled an easy and minimally invasive removal of a small abdominal wall metastasis of chromophobe renal cell carcinoma despite obesity and scars after repeat laparotomies.
1.1. Background: Neurofibromatosis type I (NFI) is a common genodermatosis, with an incidence of 1 new case to 3000-3500 live births. Described in 1882, it occurs from gene mutations of the encoding protein called neurofibrinin. NF1 patients are at increased risk for neoplasms.
Patients with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) are in hypercoagulabe state due to various coagulation abnormalities and at increased risk for thromboembolic events. We report acute upper arm ischemia caused by spontaneous thromboembolism with no identified source in a patient with HIV infection.
Biopsy of colon in a case of ulcerative recto-colitis stained with hematoxylin and eosin method showing a dilated colonic gland with the heart shape located near to a second more irregular, symmetric gland, as if this is an image reflected in a pond
- 1
- 2
ACMCR Archive
Articles Published
All articles are fully peer reviewed free to access and easy to download from our Site.
Why ACMCR?
- Highly Indexed Journals
- Fast Peer-Review System
- Reprints Issued Across the World
- Timely Submission for Indexing
- Collaboration with Research Institutions
- Reprints issued accross the world
- Diverse Subject Coverage
- DOI Assignment for Every Article
- Strict Ethical Guidelines
Digital Object Identifier

Content Registration at Crossref and DOI assignment for all published articles