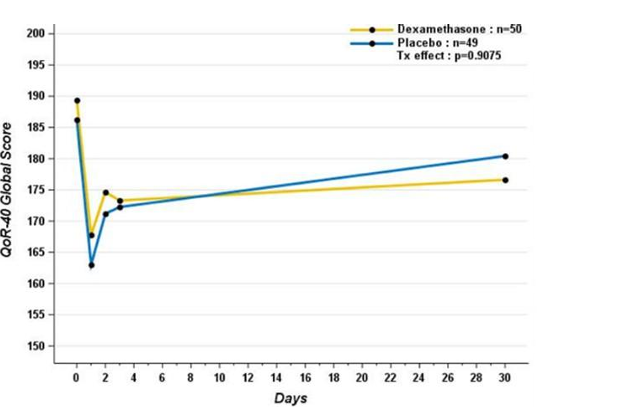
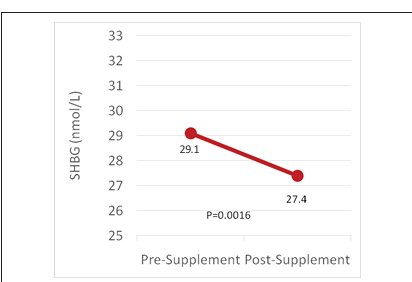
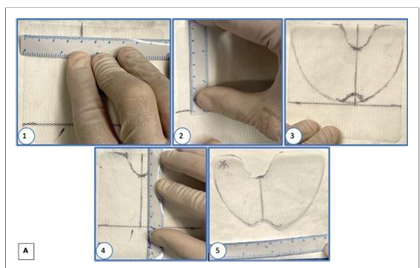
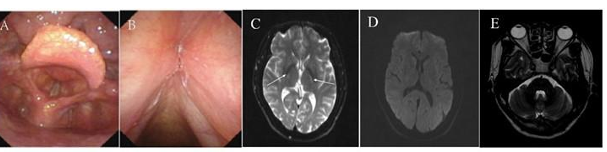
1. Introduction
G. Stigler and G. Becker, two Nobel Prize winners, state, “tastes neither change capriciously nor differ importantly between people. On this interpretation one does not argue over tastes for the same reason that one does not argue over the Rocky Mountains―both are there, will be there next year, too, and are the same to all men (AER, 1977) [1].
1. Clinical Image
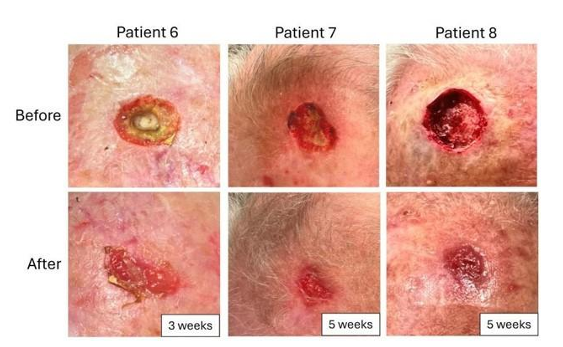
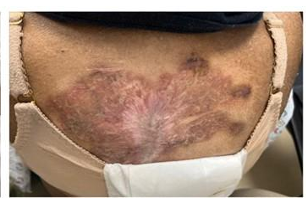
A 40-year-old woman with a history of asthma presented to the emergency department with a one-month history of fatigue, fever, and shortness of breath. The clinical examination revealed no abnormalities.
1. Abstract
1.1. Background: Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) affects about 3.6% of the US population and has clear diagnostic criteria and treatment modalities. Individuals with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and intellectual disabilities (ID) are at an elevated risk for exposure to trauma and development of PTSD.
1. Abstract
This case report discusses a 38-year-old female with a history of congenital aortic stenosis who underwent the Ross procedure and subsequent aortic valve replacement (AVR) with a biological prosthesis.
1. Introduction
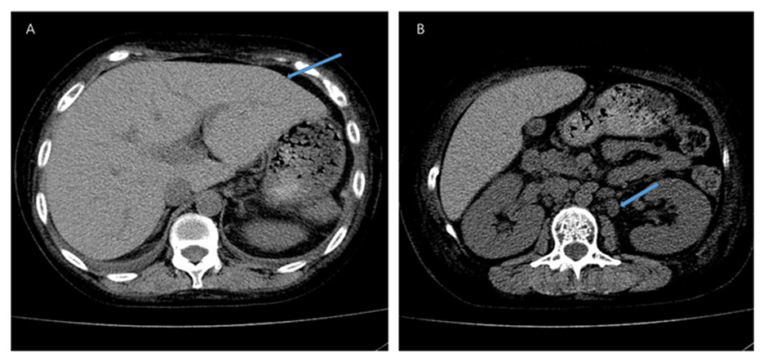
Malignant pheochromocytomas are rare endocrine tumors that develop within chromaffin tissue. The diagnosis of malignancy is based on neoplastic recurrence or the presence of metastasis in organs
that lack chromaffin tissues [1].
1. Abstract
1.1. Purpose: to study the incidence, the time of development, the etiologies, and the impact outcome of post-traumatic hypoxemia in the intensive care unit.
1. Abstract
1.1. Background: Previous studies have linked Alzheimer’s disease (AD) with cerebellar dysfunction. However, these studies lack substantial cerebellar characterization and features during AD progression.
1. Abstract
The European Medicines Authority (EMA) is a decentralised agency of the European Union (EU) responsible for the scientific evaluation, supervision and safety monitoring of medicines in the EU
and the European economic Area (EEA). On July 11th, 2023, it issued a press release stating that PRAC (The EMA’s safety committee) was reviewing data on the potential risk of suicidal thoughts and thoughts of self-harm with medicines known as GLP-1 receptor agonists, including Ozempic (semaglutide), Saxenda (liraglutide) and Wegovy (semaglutide).
1. Abstract
A classic example of the symbiosis of structural and functional perturbations is vascular occlusion due to atherosclerosis. Narrowing of the blood vessel is already a serious danger, because very often the formed elements in the blood coagulate as blood clots – larger structural formulas.
1. Case Report
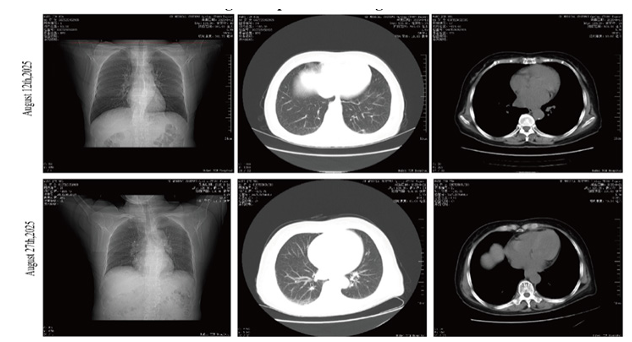
Parkinsonian syndromes are determined by the presence of at least two of the four main symptoms: bradykinesia, rigidity, resting tremor and postural instability [2, 18], caused by a reduction in dopamine in the pars Compacta of the substantia nigra [6].
ACMCR Archive
Articles Published
All articles are fully peer reviewed free to access and easy to download from our Site.
Why ACMCR?
- Highly Indexed Journals
- Fast Peer-Review System
- Reprints Issued Across the World
- Timely Submission for Indexing
- Collaboration with Research Institutions
- Reprints issued accross the world
- Diverse Subject Coverage
- DOI Assignment for Every Article
- Strict Ethical Guidelines
Digital Object Identifier

Content Registration at Crossref and DOI assignment for all published articles