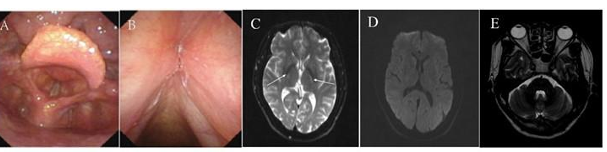
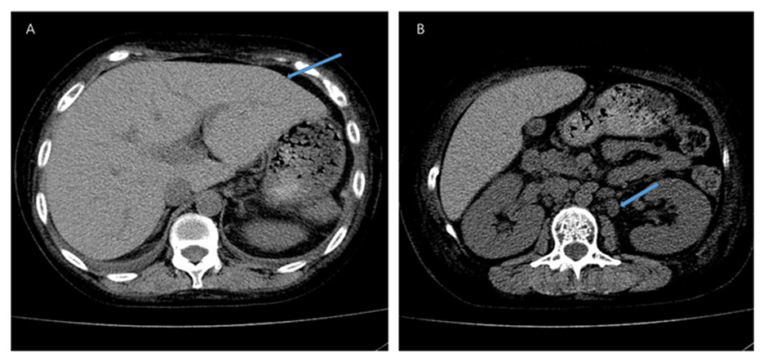
The development of pyogenic liver abscess (PLA) after liver transplant is rare. Studies have commonly reported hepatic artery thrombosis and biliary tract pathologies as risk factors for PLA formation. Whilst other modifiable etiologies include diabetes and immunosuppression. This is a case of a 71-year-old male with a history of hepatitis B, diabetes mellitus, and hepatocellular carci noma who presented with PLA formation 14 years and 21 years after successful liver transplantation without biliary tract recon struction. Post-transplant biliary cholangiopathy and hepatic ar tery thrombosis were not present in both instances. Intravenous antibiotics and abscess drainage were performed for both PLAs with complete resolution. This case highlights the importance of early recognition of liver abscess and management of diabetes mellitus glycemic control, immunosuppressive drugs, and periop erative antibiotics prophylaxis to prevent future PLA formation in post-liver transplant patients.
Medication related osteonecrosis of the jaw (MRONJ) is a debili tating condition characterized by exposure of non-healing necrotic bone lasting eight weeks or longer in the mandible or maxilla after medication use. Most commonly, MRONJ is a concern for patients receiving bisphosphonate therapy, most commonly for patients undergoing cancer treatment. The use of bisphosphonates in the treatment of osteoporosis has also been implied in the genesis of MRONJ, although at a lower rate [1]
1.1. Background: The observational link between microalbumin and type 2 diabetes (T2DM) is well established. However, it is uncertain if the link is causative. 1.2. Methods: The current study performed Mendelian random ization (MR) on publicly accessible genome-wide association study (GWAS) summary data in order to investigate the causal linkages between microalbumin and T2DM. A single set of MR analyses was performed. As instrumental variables, a dataset of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) with significance value smaller than the genome-wide criteria (5*10-8) was employed. 1.3. Results: The results suggested that microalbumin had a causal influence on T2DM risk based on the 0.05 threshold. Microalbu min was shown to be positively linked with the risk of T2DM using the inverse variance weighted (IVW) technique (OR = 1.346, 95% CI, 1.062-1.706, P = 0.014). The weighted median MR estimations revealed that microalbumin was positively associated with the in cidence of T2DM (OR = 1.356, 95% CI, 1.038-1.771, P = 0.0254). 1.4. Conclusions: The data showed that microalbumin may in crease the incidence of T2DM dependent on the genome-wide statistical significance level. This study supports the notion that microalbumin has a negative causal influence on T2DM risk.
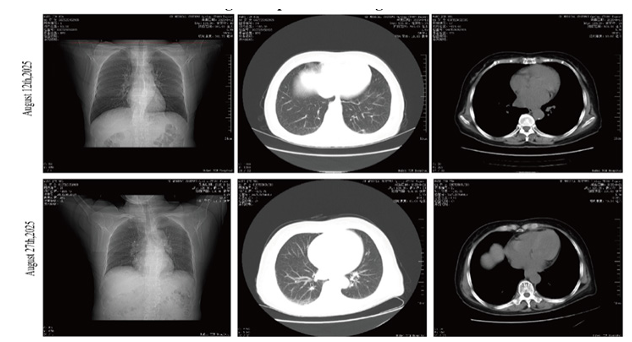
Currently, the primary approach for treating patent ductus arterio sus (PDA) is an alternative non-surgical strategy. Various devices are used for transcatheter closure of PDA. However, the emboli zation of these percutaneous devices is a rare yet severe complica tion. In this case, a 12-year-old girl underwent a successful attempt to close her PDA using an Amplatzer device. At the next morning echocardiography control, the device was found to be dislodged and migrated to the right pulmonary artery
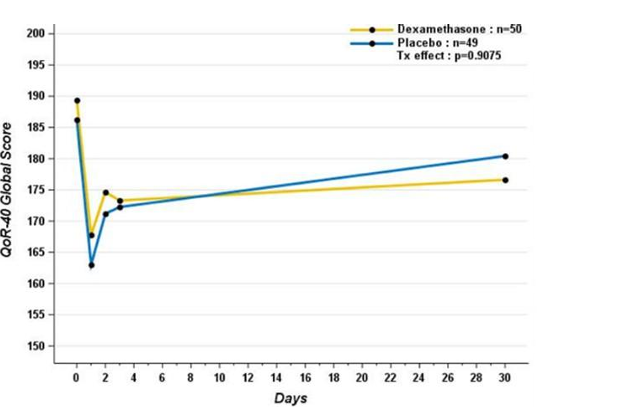
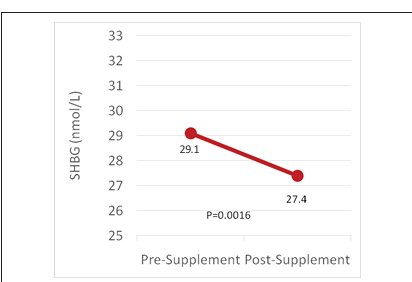
1.1. Background: Type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension are two important public health challenges, and both are linked to increased risk of cardiovascular events. Hyperuricemia has re cently emerged as an independent risk factor in the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension through several pro posed mechanisms. These include endothelial dysfunction leading to vascular remodeling, inhibition of proliferation and migration of endothelial cells and NO secretion, formation of peroxynitrite through uric acid depended reactive oxygen species and NO and promoting L-arginine degradation. As a result of the effects of hy perglycemia and neurohormonal activation, UA levels are inde pendently associated with endothelial dysfunction in animals and humans, thereby promoting hypertension.[12] This study was un dertaken to find out the possible association of hyperuricemia and nitric oxide on patients with diabetes and hypertension. 1.2. Methods and Materials: The study was carried in a medical college of South India with a sample size of 186 patients which were divided into 4 groups – Group 1- healthy patients, Group 2 – patients with DM, Group 3- patients with DM and HTN, and Group 4 – patients with CAD with DM. Blood samples for serum uric acid , fasting blood sugar, nitric oxide and HbA1c and anthro pometric measurements ( height and weight for BMI) were taken. The data obtained was analyzed with IBM SPSS Statistics for Win dows, Version 20.0., IBM Corp., Chicago, IL and t-test was used to compare the results of various parameters among the studied groups. Linear regression analysis (Person correlation coefficient, r) was performed for determining the degree of association be tween different parameters. All values expressed as mean±SD, and P values of
Human height is determined by genetics and “supply of inputs to health” (Steckel, 1995) [1]. In most econometric investigations, mean height of young adults is regressed against average supply(- consumption) of essential nutrients, such as animal protein, in the final stage of human growth, say the late-adolescents (Baten, 2009; Beer, 2012; Grasgruber et al.,2016; etc.) [2-4]. A number of human biologists refer to the importance of “the first years of life”, including the gestation period (Cole, 2003; Deaton, 2007; also many pediatricians)[5, 6]. A recent human biology study con cludes, “most of the height increment seen in adults had already accrued to the age 1.5 years” (Cole and Mori, 2017) [7]. The A/P/C approach contains cohort elements which cover the supply of in puts to health from birth to the current years of investigation on top of elements of age and period. This study analyzes a series of mean height surveys by age, male and female, provided by CNSSCH [8], Chinese government, 1985 through 2019, by five-year inter vals. There are two models at hand, Bayesian(Nakamura, 1986) [9] and IT(Yang Y. et al., 2008) [10]1. 1 For the past decades, the author has employed these two models in running cohort analyses of consumption of various food prod ucts with technical advice from mathematical statisticians (Clason; Saegusa). He is in no position to assert which model is superior. Whenever he had problems in running the programs, Clason and Saegusa have assisted him, in upgrading or refining the Bayesian programs [11, 12].
1.1. Background: Stroke-like migraine attacks after radiation therapy [SMART] syndrome is a rare and delayed complication of radiation therapy to the brain. Less than 100 cases have been de scribed in literature since it was first reported in 1995. On average, presentation is about more than 20 years after radiotherapy and pa tient normally present with stroke-like deficits, epileptic seizures and migraine. MRI is characteristic for unilateral and mainly pari eto-occipital cortical hyperintensities and gyriform enhancement. The importance of characterizing this syndrome for prompt recog nition and diagnosis is essential to avoid unnecessary biopsies and provide reassurance to the patient. 1.2. Case Description: We describe a 49-years-old female treated with craniospinal radiation for a IV ventricle tumor. 29 years later she was admitted in our hospital presenting migraine-like attacks, behavioral changes, bilateral loss of vision, seizures, confusion and gait instability. 1.3. Conclusions: As the global cancer survival rates improved considerably during last decades, long-term side effects of com plementary treatment as radiotherapy are likely to be more oftenly observed. SMART syndrome represents a characterizable and a distinguishable entity which can be differentiated from tumor re currence. The knowledge and awareness of this syndrome would substantially avoid unnecessary aggressive investigations and would significantly improve patient expectation and management.
1.1. Objectives: Hearing loss, the second most frequent sensori neural impairment, could be associated with missense mutations in several genes involved in the development of hearing parts. The re ceptor tyrosine kinase fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1) is known to be expressed in the inner ear and plays an important role in the formation of auditory-sensory epithelium. There have been some reports of FGFR1 gene mutations causing hearing loss. Using Whole Exome Sequencing (WES), we identified a novel mutation in the FGFR1 gene in a 30-year-old Iranian woman. 1.2. Material and Methods: Whole Exome Sequencing (WES) was performed on a 30-year-old woman, followed by sanger se quencing to check for the new mutation in her parents. PolyPhen-2 and Mupro in silico studies were performed to identify probable changes in wild-type and mutant structures. 1.3. Results: WES analysis showed a novel mutation in FGFR1 (NM 023110: exon18:c.G2313A:p.M771I) in the case. Her par ents’ Sanger sequencing revealed heterozygosity in her father and homozygosity of the normal allele in her mother. In silico inves tigations revealed no significant differences in pathogenic effects. 1.4. Conclusion: Altogether, our findings revealed no pathogen ic effect of the new mutation (M771I) of the FGFR1 gene in an Iranian 30-year-old woman. Because of hearing loss importance in preclinical diagnosis, this benign variant could help with the FGFR1 role on hearing loss in future pregnancies.
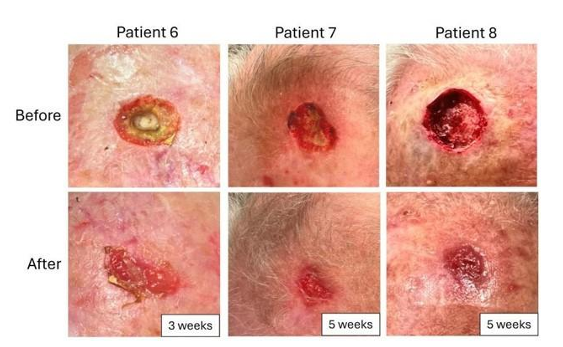
Frequency of pin tract infection among patients with tibia fracture treated with AO external fixator
1.1. Introduction: The management of open tibial fractures re mains a challenge for the orthopedic surgeons as various post-op erative complications are associated with external fixation of tibia fracture. 1.2. Objectives: To determine frequency of pin track infection among patients with tibia fracture treated with AO external fixator. 1.3. Material and Methods: This Descriptive case series study was carried out Department of Orthopedics, Medical Teaching In stitute Lady Reading Hospital from February , 2022 till December, 2022 on 110 Patients, aged 20 to 60 years of either gender with open fracture tibia Gustillo-Anderson type II or type IIIA were enrolled using non-probability consecutive sampling technique. All patients with tibia fracture underwent AO external fixation and reduction. Frequency of pin tract infection was noted. Data was entered and analyzed using SPSS 22. 1.4. Results: In our study 110 patients were enrolled with mean age of 36.7±11.5 years. There were 56.4% males and 43.6% fe male patients. Mean duration of injury was 14.6±7.6 hours. Hy pertension was present in 30.9% patients. Diabetes was present in 16.4% patients. Smoking was present in 36.4% patients. Obesity was present in 41.6% patients. Pin tract infection was present in 16.4% patients. 1.5. Conclusion: Our study concludes that the incidence of pin tract infection is high.
1.1. Background: Previous studies reported the association of the OPRK1 gene with illicit substances, nicotine, and alcohol. The present study aimed to look at the methylation levels of OPRK1 gene promoter among smokers and addicts who underwent metha done maintenance treatment (MMT). 1.2. Methods: DNAs were extracted from the whole blood of all male samples including 30 smokers, 30 opium-addicted individu als undergoing methadone treatment, and 30 healthy people, and they were treated with a sodium bisulfite kit. The studied region included 53 CpG dinucleotides investigated by sequencing tech nique. 1.3. Results: Results of methylation levels in addicted individuals who underwent MMT compared with healthy people showed no difference. Also, there was no change in any CpG sites of OPRK1 gene promoter in both smokers and compared healthy controls. There was a significant difference in the mean age between opi um-dependent people and healthy controls (P=0.017). According to the findings of the statistical analysis, resident situation and li bido dysfunction were associated with methadone dose (P=0.032 and P=0.003, respectively). 1.4. Conclusion: Altogether, the study of methylation levels at OPRK1 gene promoter was not significant among smokers and in dividuals who underwent MMT compared to the healthy controls; additionally, methadone dosage had significant associations with demographical statuses in the MMT group.
ACMCR Archive
Articles Published
All articles are fully peer reviewed free to access and easy to download from our Site.
Why ACMCR?
- Highly Indexed Journals
- Fast Peer-Review System
- Reprints Issued Across the World
- Timely Submission for Indexing
- Collaboration with Research Institutions
- Reprints issued accross the world
- Diverse Subject Coverage
- DOI Assignment for Every Article
- Strict Ethical Guidelines
Digital Object Identifier

Content Registration at Crossref and DOI assignment for all published articles