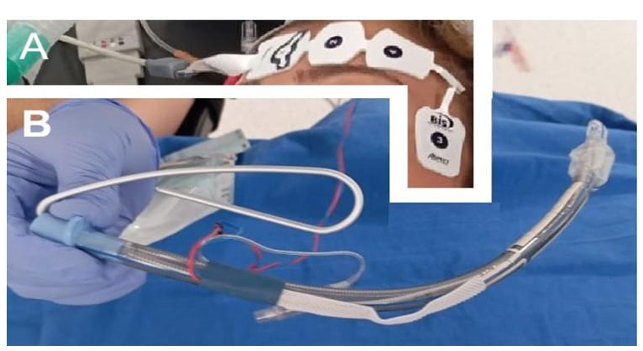
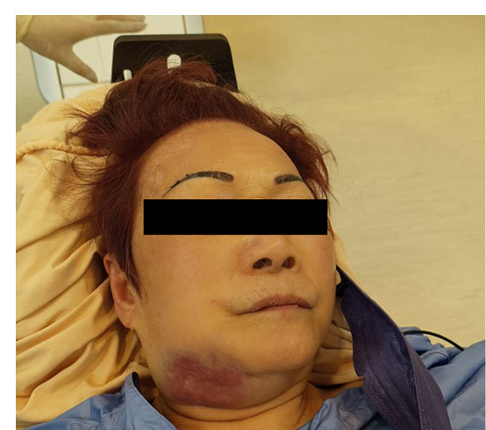
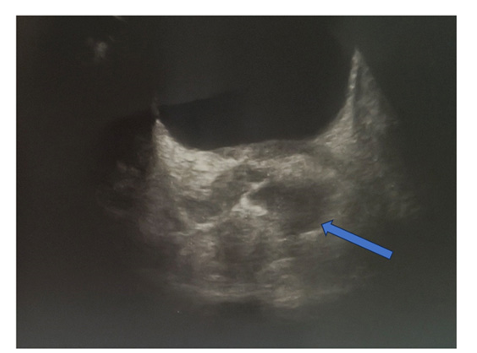
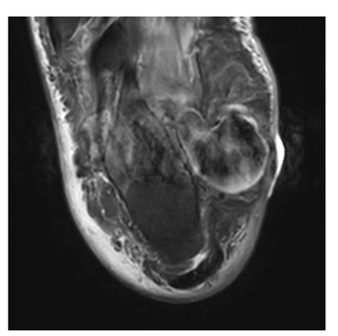
Human height is determined by genetics and “supply of inputs to health” (Steckel, 1995) [1]. In most econometric investigations, mean height of young adults is regressed against average supply(- consumption) of essential nutrients, such as animal protein, in the final stage of human growth, say the late-adolescents (Baten, 2009; Beer, 2012; Grasgruber et al.,2016; etc.) [2-4]. A number of human biologists refer to the importance of “the first years of life”, including the gestation period (Cole, 2003; Deaton, 2007; also many pediatricians)[5, 6]. A recent human biology study con cludes, “most of the height increment seen in adults had already accrued to the age 1.5 years” (Cole and Mori, 2017) [7]. The A/P/C approach contains cohort elements which cover the supply of in puts to health from birth to the current years of investigation on top of elements of age and period. This study analyzes a series of mean height surveys by age, male and female, provided by CNSSCH [8], Chinese government, 1985 through 2019, by five-year inter vals. There are two models at hand, Bayesian(Nakamura, 1986) [9] and IT(Yang Y. et al., 2008) [10]1. 1 For the past decades, the author has employed these two models in running cohort analyses of consumption of various food prod ucts with technical advice from mathematical statisticians (Clason; Saegusa). He is in no position to assert which model is superior. Whenever he had problems in running the programs, Clason and Saegusa have assisted him, in upgrading or refining the Bayesian programs [11, 12].
1.1. Background: Stroke-like migraine attacks after radiation therapy [SMART] syndrome is a rare and delayed complication of radiation therapy to the brain. Less than 100 cases have been de scribed in literature since it was first reported in 1995. On average, presentation is about more than 20 years after radiotherapy and pa tient normally present with stroke-like deficits, epileptic seizures and migraine. MRI is characteristic for unilateral and mainly pari eto-occipital cortical hyperintensities and gyriform enhancement. The importance of characterizing this syndrome for prompt recog nition and diagnosis is essential to avoid unnecessary biopsies and provide reassurance to the patient. 1.2. Case Description: We describe a 49-years-old female treated with craniospinal radiation for a IV ventricle tumor. 29 years later she was admitted in our hospital presenting migraine-like attacks, behavioral changes, bilateral loss of vision, seizures, confusion and gait instability. 1.3. Conclusions: As the global cancer survival rates improved considerably during last decades, long-term side effects of com plementary treatment as radiotherapy are likely to be more oftenly observed. SMART syndrome represents a characterizable and a distinguishable entity which can be differentiated from tumor re currence. The knowledge and awareness of this syndrome would substantially avoid unnecessary aggressive investigations and would significantly improve patient expectation and management.
1.1. Objectives: Hearing loss, the second most frequent sensori neural impairment, could be associated with missense mutations in several genes involved in the development of hearing parts. The re ceptor tyrosine kinase fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1) is known to be expressed in the inner ear and plays an important role in the formation of auditory-sensory epithelium. There have been some reports of FGFR1 gene mutations causing hearing loss. Using Whole Exome Sequencing (WES), we identified a novel mutation in the FGFR1 gene in a 30-year-old Iranian woman. 1.2. Material and Methods: Whole Exome Sequencing (WES) was performed on a 30-year-old woman, followed by sanger se quencing to check for the new mutation in her parents. PolyPhen-2 and Mupro in silico studies were performed to identify probable changes in wild-type and mutant structures. 1.3. Results: WES analysis showed a novel mutation in FGFR1 (NM 023110: exon18:c.G2313A:p.M771I) in the case. Her par ents’ Sanger sequencing revealed heterozygosity in her father and homozygosity of the normal allele in her mother. In silico inves tigations revealed no significant differences in pathogenic effects. 1.4. Conclusion: Altogether, our findings revealed no pathogen ic effect of the new mutation (M771I) of the FGFR1 gene in an Iranian 30-year-old woman. Because of hearing loss importance in preclinical diagnosis, this benign variant could help with the FGFR1 role on hearing loss in future pregnancies.
Frequency of pin tract infection among patients with tibia fracture treated with AO external fixator
1.1. Introduction: The management of open tibial fractures re mains a challenge for the orthopedic surgeons as various post-op erative complications are associated with external fixation of tibia fracture. 1.2. Objectives: To determine frequency of pin track infection among patients with tibia fracture treated with AO external fixator. 1.3. Material and Methods: This Descriptive case series study was carried out Department of Orthopedics, Medical Teaching In stitute Lady Reading Hospital from February , 2022 till December, 2022 on 110 Patients, aged 20 to 60 years of either gender with open fracture tibia Gustillo-Anderson type II or type IIIA were enrolled using non-probability consecutive sampling technique. All patients with tibia fracture underwent AO external fixation and reduction. Frequency of pin tract infection was noted. Data was entered and analyzed using SPSS 22. 1.4. Results: In our study 110 patients were enrolled with mean age of 36.7±11.5 years. There were 56.4% males and 43.6% fe male patients. Mean duration of injury was 14.6±7.6 hours. Hy pertension was present in 30.9% patients. Diabetes was present in 16.4% patients. Smoking was present in 36.4% patients. Obesity was present in 41.6% patients. Pin tract infection was present in 16.4% patients. 1.5. Conclusion: Our study concludes that the incidence of pin tract infection is high.
1.1. Objective: To assess the postoperative healing of patients with distal radius fractures treated with wrist arthroscopy-assisted small incision and its effect on wrist function using CT images combined with Logistic multiple regression analysis. 1.2. Methods: 166 patients with distal radius fracture were ran domly divided into control group (open reduction and internal fixation) and study group (wrist arthroscopy-assisted small inci sion treatment), with 83 cases for each group. All patients under went postoperative CT examination, Logistic multiple regression analysis was used to assess the recovery of wrist function, and the postoperative healing of the two groups was also assessed and compared. 1.3. Results: The operation time of the study group was longer than that of the control group, and the intraoperative blood loss and hospitalization time were less than those of the control group (P < 0.05); the fracture wound healing time in study group was shorter than that in control group, and disabilities of the arm, shoulder, and hand (DASH) score at 3 and 6 months after operation in study group was lower than that in control group (P < 0.05); the pain se verity, psychological status, independent ability, and life comfort score at 1, 3, and 6 months after operation in both groups were higher than those before treatment, and the score in study group was higher than that in control group (P < 0.05); CT image found that the palmar inclination angle and ulnar deviation angle in study group were greater than those in control group (P < 0.05). Logistic multiple regression analysis showed that operation time and blood loss could be used as independent factors affecting postoperative fracture healing and wrist joint function recovery in both groups (P
1.1. Objective: Gitelman syndrome (GS) is an autosomal reces sive tubular disorder characterized by metabolic alkalosis, hypo kalemia, hypomagnesemia and hypocalciuria. GS is mostly caused by inactivating mutations of the SLC12A3 gene. The purpose of this study was to describe the clinical features of a GS patient and investigate the underlying mutations of SLC12A3 gene in the ped igree. 1.2. Methods: A patient suffering from muscle weakness was clin ically diagnosed as GS. Clinical data of the proband were studied retrospectively. All of his family members were screened for SL C12A3 gene mutations. 26 exons and exon-intron boundaries of SLC12A3 gene were amplified by Polymerase Chain Reaction(P CR). PCR products were sequenced directly. 1.3. Results: The proband had hyperreninemia but hypoaldoster onemia, which was distinct from the cases previously reported. The proband and his sick brother were found to have the same compound heterozygous mutations (c.917C>T and IVS 14-8T>C) of SLC12A3 gene. Each mutation was detected in paternal and maternal genomic DNA, respectively. The proband’s healthy brother had one mutation (c.917C>T) only. IVS 14-8T>C was a novel splicing site mutation that had never been reported. 1.4. Conclusion: Hypoaldosteronemia was found in a GS patient. A novel heterozygous splicing site mutation of the SLC12A3 gene was reported, expanding the spectrum of SLC12A3 gene muta tions.
Closed reduction and percutaneous pinning under image intensifi er is now the treatment of choice for most of the displaced supra condylar fractures of the humerus in children. 1.1. Objective: To compare the functional outcomes of above el bow backslab versus close reduction and percutaneous pinning in supracondylar humerus fracture in kids. 1.2. Materials And Methods: This Randomized Controlled Trial was conducted in the Department of Orthopedics, Lady Reading Hospital, Peshawar Pakistan from October 2022 to April 2023 on sixty patients (30 patients with closed reduction and percutaneous pinning = Group A, 30 patients with closed reduction and back slab= Group). Non – Probability Consecutive Sampling Technique was used. Patient age 5 to 14 years, Both genders and Patients pre senting within 48 hours after trauma with Gartland III supracondy lar humerus fracture as per operational definition were included in the study while Patients with open fracture, Patients with vascular injury and Patients with multiple humerus fractures were excluded from the study. 1.3. Results: Age of the patients ranged from 5 to 14 years. Mean age of the patients who received CRPP was 10.04±2.014 years while mean age of the patients who received Backslab was 11.04±1.323 years. Excellent outcomes were observed in 19 pa tients (63.3%) in CRPP group versus 17 patients (56.7%) in back slab group. 1.4. Conclusion: In pediatric patients presenting with type II and III supracondylar fractures, when compared to backslab, CRPP was associated with higher overall satisfactory results according to Flynn’s criteria.
Interleukin-6(IL-6) and CRP have been involved in anti-inflam matory reaction and autoimmune diseases. Interleukin is known for enabling cancer growth and is essential for tumour-directed immune response. CRP modulates inflammatory responses and stimulate platelet and leukocyte responses associated with acute phase responses to tumour growth. Its accumulation in blood is as sociated with a low-level inflammatory response and is indicative of advancing disease, as occurs in cancer
Sinonasal lymphoepithelial carcinoma (SLEC) is an extremely rare malignant tumor of the sinonasal tract. In this case report, we present a case with locally advanced disease of the posterior ethmoid cells. We also aim to review the clinical, radiological and pathological features, as well as the available treatment strategies, contributing to the literature of this rare malignancy. Our patient presented with unilateral nasal congestion, discharge, recurrent epistaxis, aural fullness, diplopia and visual disturbance. Imaging revealed an extensive osteolytic lesion of the right nasal cavity with intraorbital and intracranial invasion. Histopatholog ical examination of posterior ethmoid cell mucosa demonstrated undifferentiated malignant cells, associated with lymphoplasma cytic infiltration, while the immunohistochemistry was positive for pancytokeratin. A final diagnosis of EBV-positive SLEC was rendered and the patient was treated with concomitant chemo-ra diotherapy. To our knowledge, this is the first case report of SLEC arising from the posterior ethmoid cells with invasion into the orbit and middle cranial fossa.
As stated in the current World Health Organization classification, T-lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma is a neoplasm of lympho blasts committed to T-cell lineage involving bone marrow (BM), blood, or presenting as a tissue-based mass involving the thymus, lymph nodes, or extranodal sites. We present a 10 -year -old boy who is a family -burdened mucoviscidosis. Imaging studies report an extended anterior mediastinum. After the first biopsy, the final diagnosis is difficult, which significantly slows down the neces sary treatment. Prolonged treatment with corticosteroids and a heterozygous family-burdened mucoviscidosis is the cause of se vere chemotoxicity after one course of chemotherapy. This is the reason for the completion of treatment by consolidating involved site radiоtherapy. The primary thymic Non-Hodgkin lymphoma is a rare disease. Diagnosis is extremely difficult and requires a biopsy of the tu mor and bone marrow, strictly pathohistological and immunohis tochemical analysis, as well as imaging studies involving CT and PET/CT. The clinical case focuses on the difficult final diagnosis, as well as the need for consolidating involved site radiotherapy of mediastinal tumor mass with a radical dose with strictly preserving the adjacent normal tissues and organs.
ACMCR Archive
Articles Published
All articles are fully peer reviewed free to access and easy to download from our Site.
Why ACMCR?
- Highly Indexed Journals
- Fast Peer-Review System
- Reprints Issued Across the World
- Timely Submission for Indexing
- Collaboration with Research Institutions
- Reprints issued accross the world
- Diverse Subject Coverage
- DOI Assignment for Every Article
- Strict Ethical Guidelines
Digital Object Identifier

Content Registration at Crossref and DOI assignment for all published articles