Chromophobe RCC In Sacral Ectopic Kidney: Integrating Case Insights with A Review of Renal Ectopia Malignancies
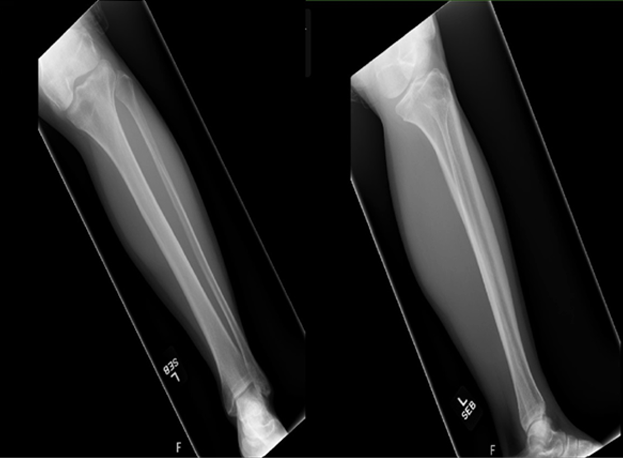
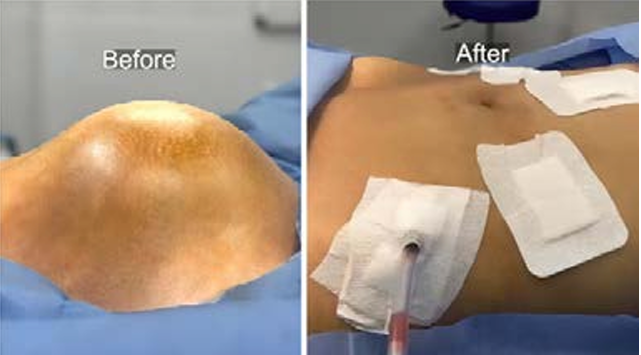
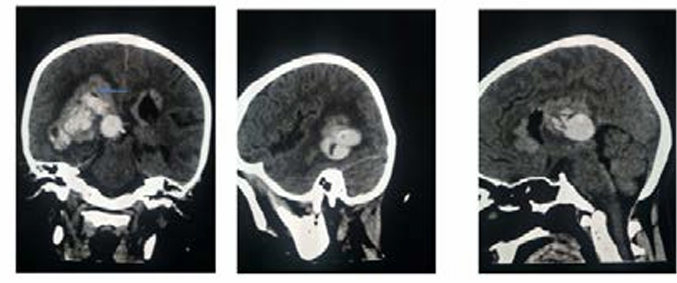
Renal ectopia is a rare condition where a kidney is not in its usual position, often found incidentally. When renal cell carcinoma (RCC) occurs in such kidneys, especially in the sacral area, it poses significant challenges.